There’s a irritating reality that each enterprise offers with early into its development: Extra money, extra issues.
It appears counterintuitive — if gross sales and income are up, isn’t {that a} good factor? How are greater earnings a possible drawback?
Put merely, all of it comes all the way down to the truth that the extra you promote, the extra money it’s essential spend. This consists of advertising and marketing and gross sales campaigns to achieve extra prospects, the manufacturing prices of extra items, and the money and time required for brand new product improvement.
Often called variable value, this gross sales/spend ratio is one thing each enterprise proprietor ought to perceive, however on-line recommendation listicles and motion plans usually assume readers have an intrinsic data of this idea slightly than offering a working definition.
On this piece, we’ll clear up variable value confusion: Right here’s what it’s essential learn about variable prices, learn how to calculate them, and why they matter.

What’s a variable value?
Variable prices are the sum of all labor and supplies required to supply a unit of your product. Your whole variable value is the same as the variable value per unit, multiplied by the variety of items produced. Your common variable value is the same as your whole variable value, divided by the variety of items produced.
Let’s study every of those elements in additional element.
Variable Value Per Unit
The variable value per unit is the quantity of labor, supplies, and different assets required to supply your product. For instance, if your organization sells units of kitchen knives for $300 however every set requires $200 to create, check, package deal, and market, your variable value per unit is $200.
Variety of Models Produced
The variety of items produced is precisely what you would possibly count on — it’s the whole variety of objects produced by your organization. So in our knife instance above,when you’ve made and offered 100 knife units your whole variety of items produced is 100, every of which carries a $200 variable value and a $100 potential revenue.
Variable Value Method
To calculate variable prices, multiply what it prices to make one unit of your product by the whole variety of merchandise you’ve created. This method appears like this: Complete Variable Prices = Value Per Unit x Complete Variety of Models.
Variable prices earn the identify as a result of they will improve and reduce as you make kind of of your product. The extra items you promote, the extra money you’ll make, however a few of this cash might want to pay for the manufacturing of extra items. So, you’ll want to supply extra items to really flip a revenue.

And, as a result of every unit requires a specific amount of assets, the next variety of items will elevate the variable prices wanted to supply them.
Variable prices aren’t a “drawback,” although — they’re extra of a needed evil. They play a task in a number of bookkeeping duties, and each your whole variable value and common variable value are calculated individually.
Complete Variable Value
Your whole variable value is the sum of all variable prices related to every particular person product you’ve developed. Calculate whole variable value by multiplying the associated fee to make one unit of your product by the variety of merchandise you’ve developed.

For instance, if it prices $60 to make one unit of your product and also you’ve made 20 items, your whole variable value is $60 x 20, or $1,200.
Common Variable Value
Your common variable value makes use of your whole variable value to find out how a lot, on common, it prices to supply one unit of your product. You may calculate it with the method under.
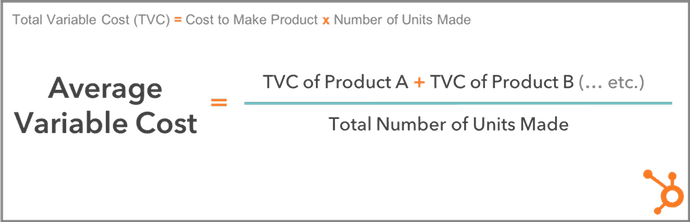
Complete Variable Value vs. Common Variable Value
If the common variable value of 1 unit is discovered utilizing your whole variable value, don’t you already understand how a lot one unit of your product prices to develop? Can’t you’re employed backward, and easily divide your whole variable value by the variety of items you’ve gotten? Not essentially.
Whereas whole variable value exhibits how a lot you’re paying to develop each unit of your product, you may also should account for merchandise which have completely different variable prices per unit. That’s the place common variable value is available in.
For instance, in case you have 10 items of Product A at a variable value of $60/unit, and 15 items of Product B at a variable value of $30/unit, you’ve gotten two completely different variable prices — $60 and $30. Your common variable value crunches these two variable prices down to 1 manageable determine.
Within the above instance, you will discover your common variable value by including the whole variable value of Product A ($60 x 10 items, or $600) and the whole variable value of Product B ($30 x 15 items, or $450), then dividing this sum by the whole variety of items produced (10 + 15, or 25).
Your common variable value is ($600 + $450) ÷ 25, or $42 per unit.
Variable vs. Mounted Value
The alternative of variable value? Mounted value. Mounted prices are prices that don’t change in response to the variety of merchandise you’re producing.
Some widespread fastened prices embody renting or leasing a constructing, utility payments, web site internet hosting, enterprise mortgage repayments, and property taxes.
Value noting? These prices aren’t static — that means, your hire could improve yr over yr. As an alternative, they continue to be fastened solely in reference to product manufacturing.
To calculate the common fastened value, use this method:

Each variable and glued prices are important to getting an entire image of how a lot it prices to supply an merchandise — and the way a lot revenue stays after every sale.
What’s the variable value ratio?
The variable value ratio permits companies to pinpoint the connection between variable prices and internet gross sales. Calculating this ratio helps them account for each the rising income in addition to rising manufacturing prices, in order that the corporate can proceed to develop at a gradual tempo.
To calculate variable value ratio, use this method:
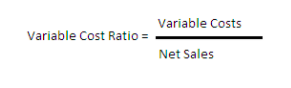
Let’s put it into follow. In case you’re promoting an merchandise for $200 (Web Gross sales) nevertheless it prices $20 to supply (Variable Prices), you divide $20 by $200 to get 0.1. Multiply by 100 and your variable value ratio is 10%. Because of this for each sale of an merchandise you’re getting a 90% return with 10% going towards variable prices.
Combining variable and glued prices, in the meantime, will help you calculate your break-even level — the purpose at which producing and promoting items is zeroed out by the mix of variable and glued prices.
Think about our instance above once more. In case your variable prices are $20 on a $200 merchandise and your fastened prices account for $100, your whole prices now account for 60% of the merchandise’s sale worth, leaving you with 40%.
Put merely? The upper your whole value ratio, the decrease your potential revenue. If this quantity turns into detrimental, you’ve handed the break-even level and can begin shedding cash on each sale.
So, what’s thought-about a variable value to the enterprise?
A number of the commonest variable prices embody bodily supplies, manufacturing tools, gross sales commissions, workers wages, bank card charges, on-line fee companions, and packaging/transport prices.
Variable Value Examples
- Bodily Supplies
- Manufacturing Tools
- Gross sales Commissions
- Employees Wages
- Credit score Card Charges
- On-line Cost Companions
- Packaging and Delivery Prices
Let’s study every in additional element.
Bodily Supplies
These can embody elements, material, and even meals components required to make your remaining product.
Manufacturing Tools
In case you automate sure elements of your product’s improvement, you would possibly have to put money into extra automation tools or software program as your product line will get greater.
Gross sales Commissions
The extra merchandise your organization sells, the extra you would possibly pay in fee to your salespeople as they win prospects.
Employees Wages
The extra merchandise you create, the extra staff you would possibly want, which suggests a much bigger payroll, too.
Credit score Card Charges
Companies that obtain bank card funds from their prospects will incur increased transaction charges as they ship extra companies.
On-line Cost Companions
Apps like PayPal usually cost companies per transaction so prospects can take a look at purchases by way of the app. The extra orders you obtain, the extra you will pay to the app.
Packaging and Delivery Prices
You would possibly pay to package deal and ship your product by the unit, and subsequently extra or fewer shipped items will trigger these prices to range.
Anticipate the Surprising
Whereas variable prices, whole variable prices, common variable prices, and the variable value ratio usually appear difficult on the floor, these phrases are merely methods to characterize the altering nature of prices to supply new objects as your enterprise grows.
By understanding the character of those prices and the way they affect your present and projected income, it’s potential to higher put together for evolving market forces and scale back the affect of variable prices in your backside line.
Source link















