One thing to look ahead to: Stable-state batteries are nonetheless nebulous exterior of the lab. Nonetheless, automakers are scrambling to be the primary within the race to construct the primary electrical automotive to reap the benefits of the added power density and higher security when in comparison with lithium-ion designs. To that finish, they’re investing in firms like QuantumScape, Stable Energy, and Sakuu to develop manufacturing methods that both construct on present approaches or depend on new additive manufacturing know-how.
Earlier this yr, an MIT examine revealed that lithium-ion battery prices have fallen by greater than 97 p.c since its industrial introduction nearly 30 years in the past. Not solely that, however trade watchers are optimistic that by 2025 lithium-ion battery manufacturing capability may have tripled whereas the value per kilowatt-hour is predicted to dip under $100.
The dip has spurred automakers to get critical about making electrical vehicles, however the truth of the matter is that worth is just a part of the equation of creating it a more sensible choice for customers and the atmosphere. The significance of security can’t be overstated, as evidenced by GM’s recall final yr for greater than 68,000 Chevy Bolts. On that entrance, researchers are laborious at work creating a brand new cathode coating that not solely makes lithium-ion batteries safer however might additionally enhance their power density.
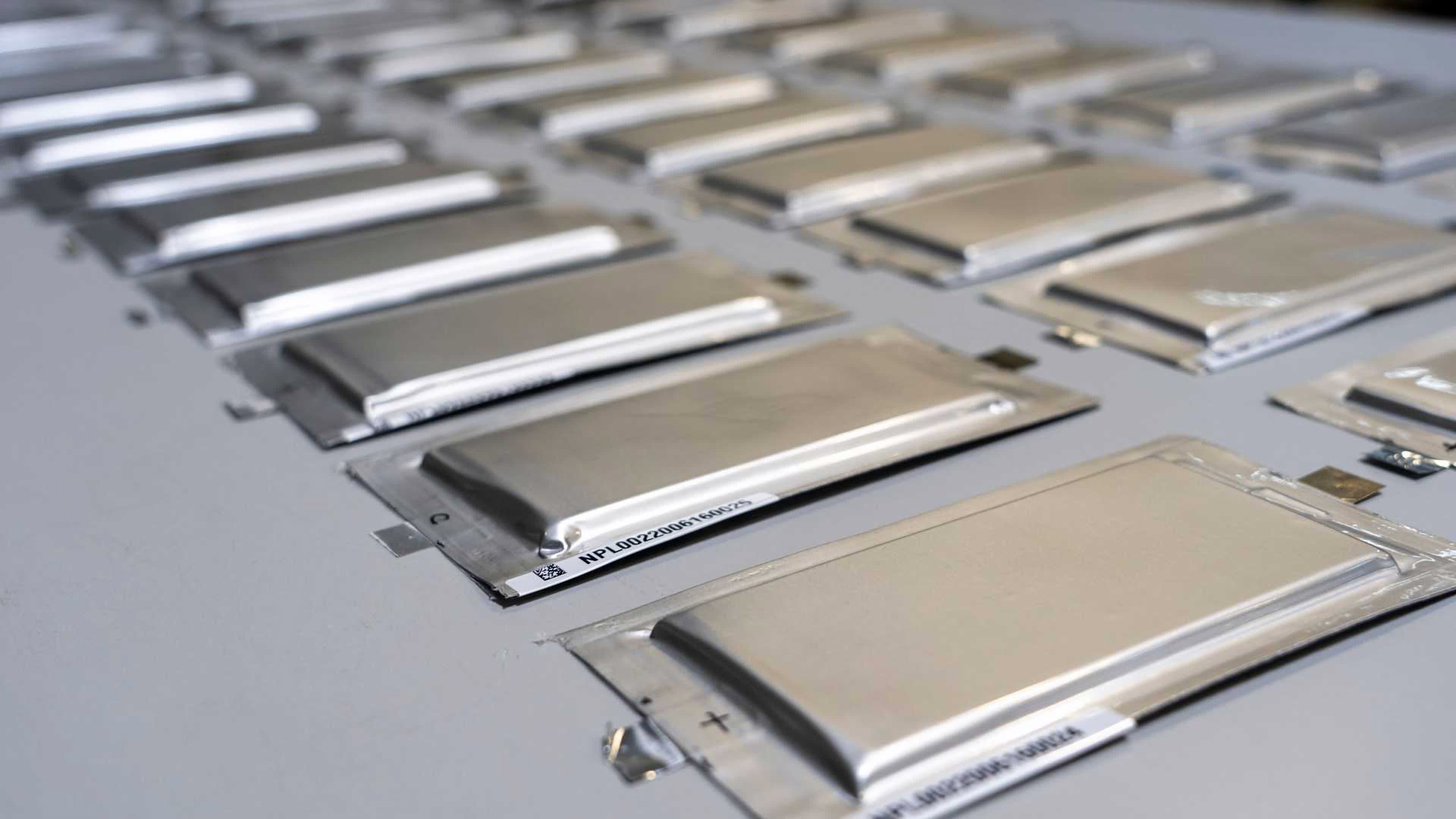
Numerous firms are banking on solid-state batteries to unravel these points. Such is the case of the 3D-printing startup known as Sakuu (previously KeraCel) that claims to have developed a lithium-metal solid-state battery that gives equal or higher efficiency in comparison with the lithium-ion batteries presently in use.
Sakuu’s cell has a capability of 3Ah and is made utilizing the corporate’s additive manufacturing know-how, set for a industrial launch within the coming months. The precise focus of the first-generation Sakuu cell is to reduce the general quantity of all the weather utilizing a binder jet printing course of developed by MIT. This methodology permits the corporate to deposit skinny layers of metallic and ceramic in a single construct.
The method is comparatively gradual, however the outcomes are batteries which can be half the dimensions and one-third the burden of their lithium-ion counterparts, which isn’t any small feat. Sakuu says it plans to start mass-producing the brand new batteries in early 2022 and is presently exploring increased voltage cathodes for an as much as 25 p.c increase in power density. The preliminary capability shall be a comparatively modest 1 GWh, but when achieved, it would symbolize a milestone within the commercialization of solid-state batteries.
One other vital issue for batteries is longevity, and this has sparked a fierce debate about how we’ll cope with lifeless batteries from electrical vehicles as they pile up. The present crop of EV batteries is not designed to be recycled. Shopper Reviews estimates these will final wherever between 100,000 to 200,000 miles earlier than their capacity to carry a cost degrades considerably. Final yr, Tesla battery provider CATL promised to start manufacturing batteries that might final for 1.24 million miles earlier than they should be changed.
Ultimately, the answer to the issue will most probably be a mixture of higher battery chemistry, progressive manufacturing, and the inventive reuse and recycling of outdated batteries.
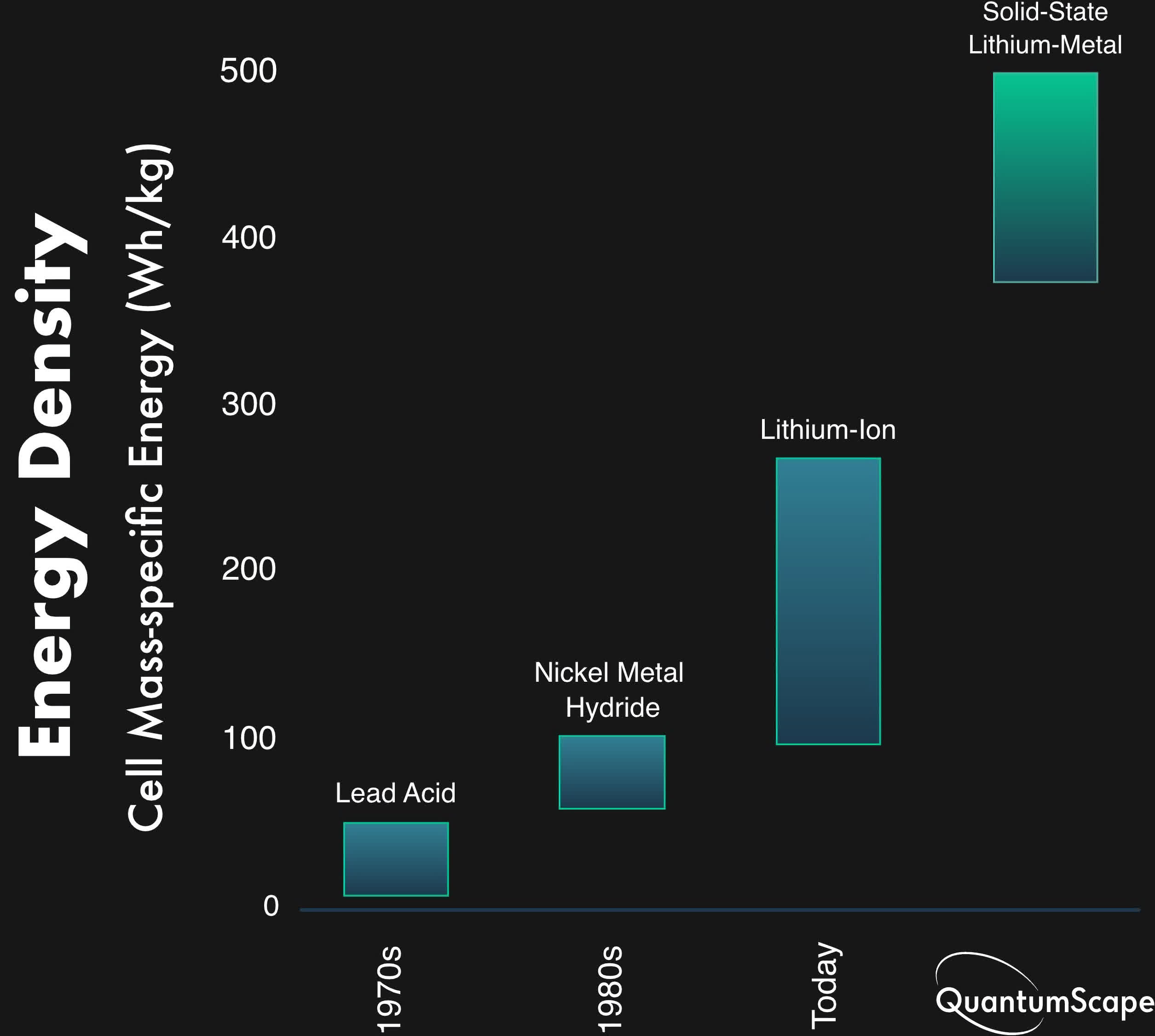
Because it stands, solid-state lithium-metal battery designs are nonetheless unproven by way of stability, regardless of providing higher power density and elevated security when in comparison with lithium-ion. Corporations like QuantumScape, Stable Energy, and Samsung say they’ve just a few options for this situation. Most are concentrating on a 2022-2023 timeline for mass manufacturing of the brand new battery cells, so it will not be lengthy earlier than we are able to see if they’re going to reside as much as the hype.
Source link















