Ahead-looking: 3D chip stacking expertise has but to reach in an enormous approach, with solely Intel Foveros reaching the market in Lakefield CPUs, and a few Zen3-with-vertically-stacked-cache merchandise ready within the wings. However at this yr’s Scorching Chips symposium, AMD is already laying out the place it intends to go from right here, with formidable concepts on apply the expertise.
The 3D V-Cache proven off by AMD at Computex is the (comparatively) easy addition of additional L3 cache to a Ryzen 9 5900X, bringing round a ~15% efficiency uplift in video games. The 3D-stacking association let AMD use a manufacturing course of that permits for extra densely packed SRAM for the higher die, becoming 64 MB within the house immediately above the 32 MB on the bottom die that needed to be silicon appropriate for each cache and compute.
This was all carried out utilizing through-silicon vias (TSVs), linked with direct vertical copper-to-copper connections that pack far nearer collectively than “conventional” microbump expertise.
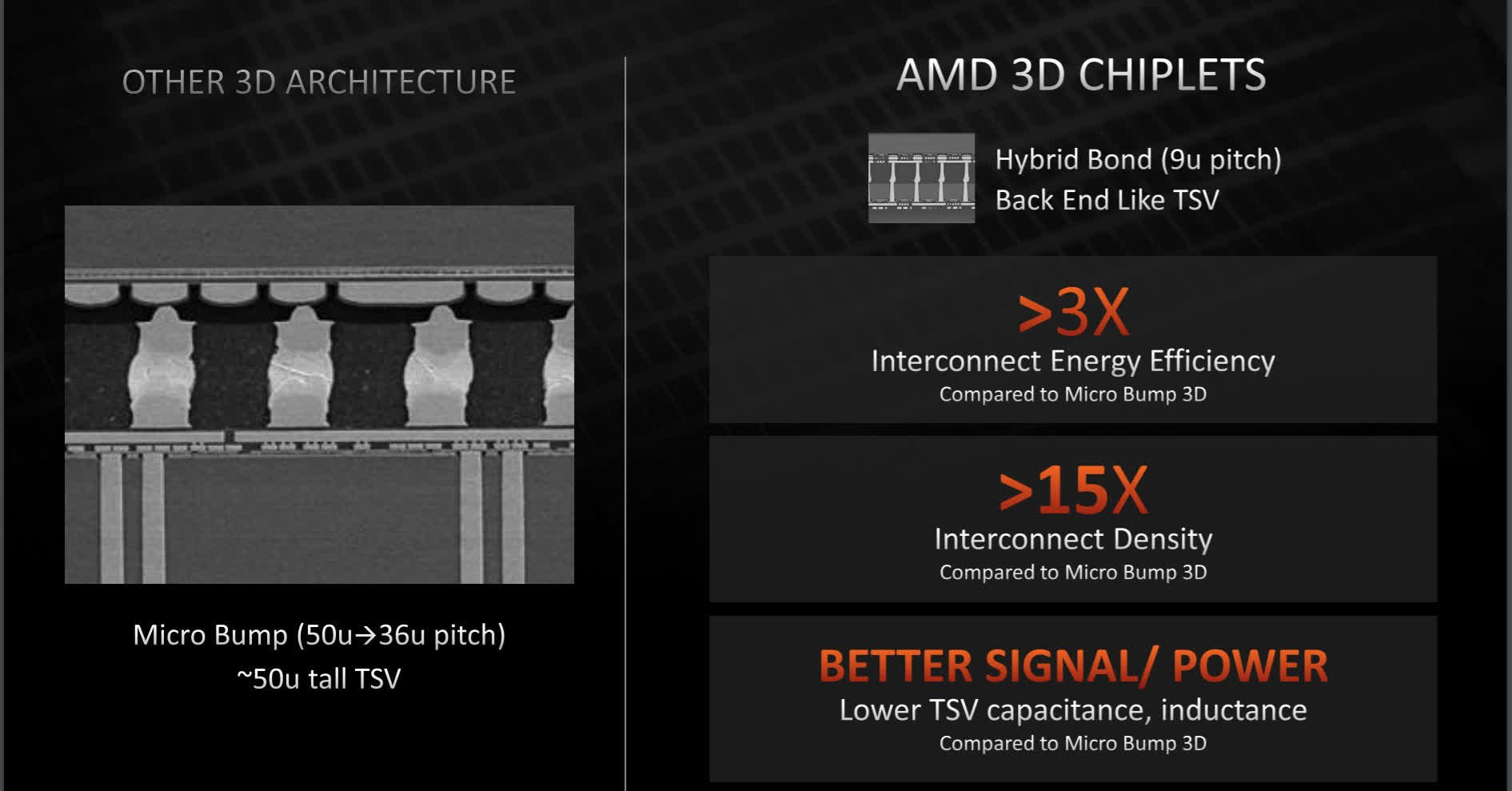
AMD claims a 9 micron bump pitch for his or her hybrid direct bonding expertise; by comparability, Intel Foveros was engaged on the order of fifty microns when applied in Lakefield, the principle level of comparability used for AMD’s declare of 3x effectivity good points and 15x larger density with its interconnects in comparison with the conspicuously unspecified “different 3D structure.”
Staff Blue even have a pitch of 36 microns quoted for his or her upcoming Foveros Omni expertise for use in Meteor Lake CPUs, and 10 microns in Foveros Direct, a hybrid resolution that extra immediately competes with what AMD’s displaying off right here.
Nonetheless, each are solely slated to reach in 2023, whereas AMD have acknowledged that their 3D-stacked Ryzen chips might be in mass-production by the tip of this yr.
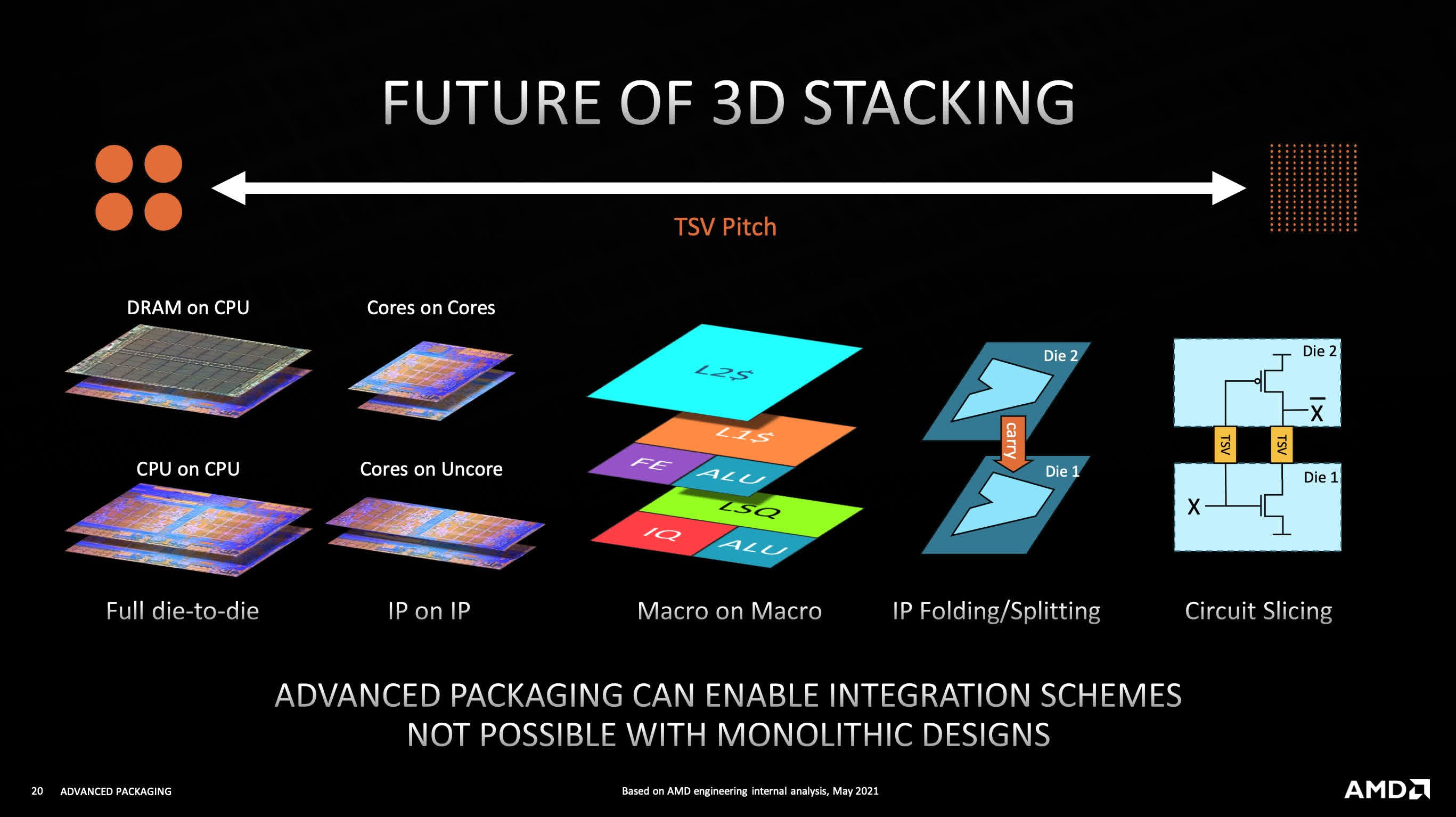
The corporate can be working with TSMC on extra complicated 3D stacking designs, with the ambition to stack CPU cores on each other, splitting macroblocks of a CPU (similar to decrease ranges of cache) between completely different layers, and even taking place to the extent of circuit slicing.
Stacking compute silicon particularly brings distinctive difficulties in offering energy to larger dies and eradicating warmth from decrease ones — one of many the reason why AMD’s 3D V-Cache is just layered on high of the bottom die’s cache, leaving the CPU cores alone.
In fact, all of this is determined by how a lot enchancment may be introduced in energy, efficiency, space and price (PPAC) metrics — and, in fact, if TSMC can proceed to ship their superior packaging methods in mass manufacturing.
Source link















